The presentation "Lactose-Functionalized Carbosilane Glycodendrimers Are Highly Potent Multivalent Ligands for Galectin-9 Binding" will be introduced by Ing. Monika Müllerová, Ph.D. from The Institute of Experimental Medicine of the CAS.
The 36th NARECOM will take place on Wednesday, May 22, 2024, at 2:30. p.m.
Join Zoom Meeting: https://cesnet.zoom.us/j/92333685068
Abstract:
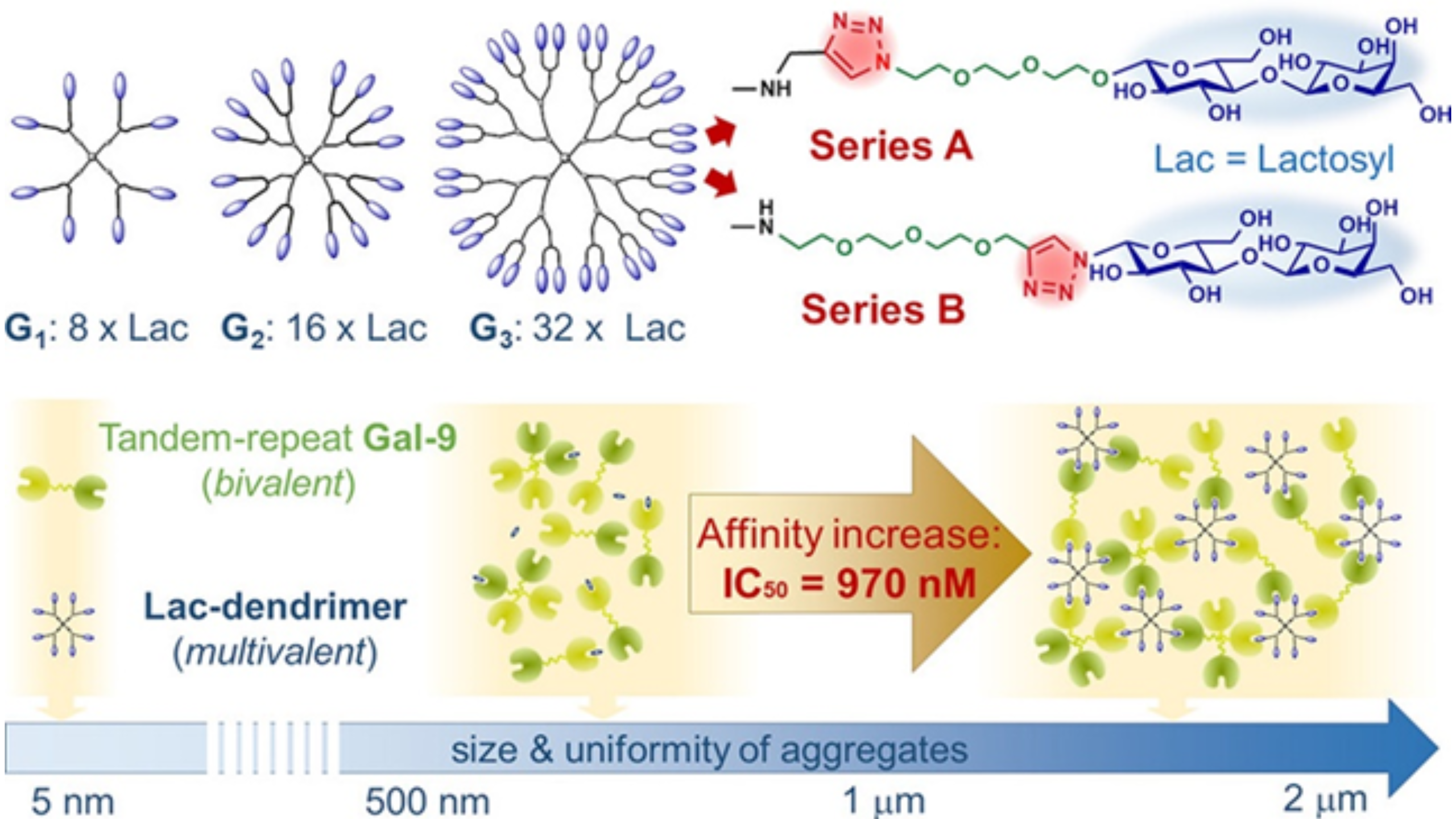
Galectins, a class of glycan-binding proteins, and their carbohydrate ligands are pivotal in modulating various biological functions. A profound comprehension of ligand-protein recognition mechanisms is imperative for advancements in galectin-targeted therapeutics1, 2. This research introduces a novel synthetic approach for lactose-functionalized carbosilane glycodendrimers (Lac-CS-DDMs) utilizing carbosilane dendrimers, the nanoscaffolds known for their minimal toxicity. Our findings highlight the exceptional affinity of these glycodendrimers, driven by dendritic effects, towards tandem-type galectins, with a notable preference for Gal-9. Quantitative analysis via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay revealed that the third-generation dendritic ligand, equipped with 32 lactose units, exhibited a remarkable binding affinity to Gal-9 (IC50 = 970 nM), outperforming monovalent lactose by a factor of 1400. This underscores the transformative potential of multivalent presentations in enhancing ligand inhibitory effects. Additionally, through dynamic light scattering measurements, we established a correlation between the augmented affinity of glycodendrimer ligands for Gal-3, Gal-8, and particularly Gal-9, and the formation of consistent and stable galectin/Lac-CS-DDM aggregates.
References:
1) Laaf, D.; Bojarová, P.; Elling, L.; Křen, V.Galectin–Carbohydrate Interactions in Biomedicine and Biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 402– 415.
2) Yoann, M. C., Roy, R. Recent Trends in Glycodendrimer Syntheses and Applications, C Top. Med. Chem. 2008, (8), 14, 1237-1285
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and The European Union - European Structural and Investments Funds in the frame of Operational Programme Research Development and Education - project Pro-NanoEnviCz (project no. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_013/0001821). The authors acknowledge the project COST LTC19049, the Czech Science Foundation project no. 23-05146S, and the Research Infrastructure NanoEnviCz (project no. LM2018124).
For more information see: